[LeetCode] 1801. Number of Orders in the Backlog
You are given a 2D integer array orders, where each orders[i] = [price, amount, orderType] denotes that amount orders have been placed of type orderType at the price price. The orderTyp is:
0 if it is a batch of buy orders, or
1 if it is a batch of sell orders.
Note that orders[i] represents a batch of amount independent orders with the same price and order type. All orders represented by orders[i] will be placed before all orders represented by orders[i+1] for all valid i.
There is a backlog that consists of orders that have not been executed. The backlog is initially empty. When an order is placed, the following happens:
If the order is a buy order, you look at the sell order with the smallest price in the backlog. If that sell order’s price is smaller than or equal to the current buy order’s price, they will match and be executed, and that sell order will be removed from the backlog. Else, the buy order is added to the backlog.
Vice versa, if the order is a sell order, you look at the buy order with the largest price in the backlog. If that buy order’s price is larger than or equal to the current sell order’s price, they will match and be executed, and that buy order will be removed from the backlog. Else, the sell order is added to the backlog.
Return the total amount of orders in the backlog after placing all the orders from the input. Since this number can be large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
Example 1: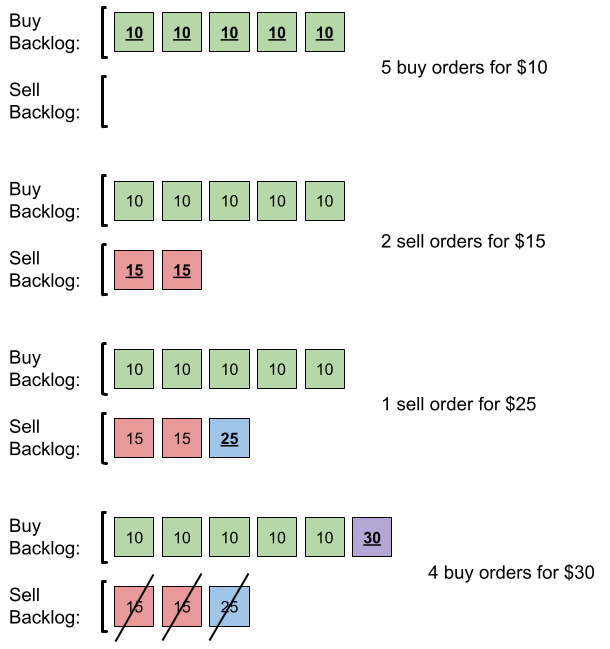
Input: orders = [[10,5,0],[15,2,1],[25,1,1],[30,4,0]]
Output: 6
Explanation: Here is what happens with the orders:
- 5 orders of type buy with price 10 are placed. There are no sell orders, so the 5 orders are added to the backlog.
- 2 orders of type sell with price 15 are placed. There are no buy orders with prices larger than or equal to 15, so the 2 orders are added to the backlog.
- 1 order of type sell with price 25 is placed. There are no buy orders with prices larger than or equal to 25 in the backlog, so this order is added to the backlog.
- 4 orders of type buy with price 30 are placed. The first 2 orders are matched with the 2 sell orders of the least price, which is 15 and these 2 sell orders are removed from the backlog. The 3rd order is matched with the sell order of the least price, which is 25 and this sell order is removed from the backlog. Then, there are no more sell orders in the backlog, so the 4th order is added to the backlog.
Finally, the backlog has 5 buy orders with price 10, and 1 buy order with price 30. So the total number of orders in the backlog is 6.
Example 2: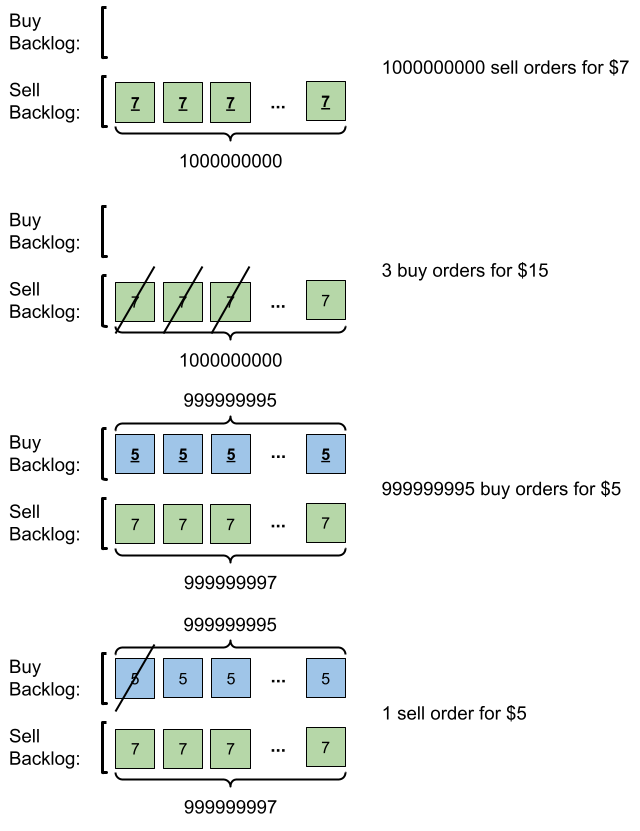
Input: orders = [[7,1000000000,1],[15,3,0],[5,999999995,0],[5,1,1]]
Output: 999999984
Explanation: Here is what happens with the orders:
- 109 orders of type sell with price 7 are placed. There are no buy orders, so the 109 orders are added to the backlog.
- 3 orders of type buy with price 15 are placed. They are matched with the 3 sell orders with the least price which is 7, and those 3 sell orders are removed from the backlog.
- 999999995 orders of type buy with price 5 are placed. The least price of a sell order is 7, so the 999999995 orders are added to the backlog.
- 1 order of type sell with price 5 is placed. It is matched with the buy order of the highest price, which is 5, and that buy order is removed from the backlog.
Finally, the backlog has (1000000000-3) sell orders with price 7, and (999999995-1) buy orders with price 5. So the total number of orders = 1999999991, which is equal to 999999984 % (109 + 7).
Constraints:
1 <= orders.length <= 105
orders[i].length == 3
1 <= pricei, amounti <= 109
orderTypei is either 0 or 1.
积压订单中的订单总数。
给你一个二维整数数组 orders ,其中每个 orders[i] = [price, amount, orderType] 表示有 amount 笔类型为 orderType 、价格为 price 的订单。订单类型 orderType 可以分为两种:
0 表示这是一批采购订单 buy
1 表示这是一批销售订单 sell
注意,orders[i] 表示一批共计 amount 笔的独立订单,这些订单的价格和类型相同。对于所有有效的 i ,由 orders[i] 表示的所有订单提交时间均早于 orders[i+1] 表示的所有订单。存在由未执行订单组成的 积压订单 。积压订单最初是空的。提交订单时,会发生以下情况:
如果该订单是一笔采购订单 buy ,则可以查看积压订单中价格 最低 的销售订单 sell 。如果该销售订单 sell 的价格 低于或等于 当前采购订单 buy 的价格,则匹配并执行这两笔订单,并将销售订单 sell 从积压订单中删除。否则,采购订单 buy 将会添加到积压订单中。反之亦然,如果该订单是一笔销售订单 sell ,则可以查看积压订单中价格 最高 的采购订单 buy 。如果该采购订单 buy 的价格 高于或等于 当前销售订单 sell 的价格,则匹配并执行这两笔订单,并将采购订单 buy 从积压订单中删除。否则,销售订单 sell 将会添加到积压订单中。
输入所有订单后,返回积压订单中的 订单总数 。由于数字可能很大,所以需要返回对 109 + 7 取余的结果。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/number-of-orders-in-the-backlog
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
思路
思路是贪心,具体做法需要用到两个堆,一个最大堆一个最小堆。题目描述里没有明确说明,但是抵消订单是没有先后顺序的,也就是说如果一张可以被抵消的订单出现的比较晚,他还是可以被合适的订单抵消掉。同时这里我们无需考虑订单抵消的合理性,比如一个 buy 订单的 price 很大,他也可以拿来抵消一个 price 很小的 sell 订单。因为我们最后考虑的只是积压订单的数量而不是数额。
我们为采购订单 buys 创建一个最大堆(相当于是买价最大的买单在顶部),为销售订单 sells 创建一个最小堆(相当于是卖价最小的订单在顶部),然后根据订单的 orderType 来区分到底是采购订单还是销售订单,把订单根据类型分别放到两个堆中。当两个堆都不为空的时候,如果最小堆堆顶元素的 sell price < 最大堆堆顶元素的 buy price,两者就可以匹配,匹配的订单数为两边订单的较小值。
复杂度
时间O(nlogn)
空间O(n)
代码
Java实现
1 | |