[LeetCode] 145. Binary Tree Postorder Traversal
Given the root of a binary tree, return the postorder traversal of its nodes’ values.
Example 1:
Input: root = [1,null,2,3]
Output: [3,2,1]
Example 2:
Input: root = []
Output: []
Example 3:
Input: root = [1]
Output: [1]
Constraints:
The number of the nodes in the tree is in the range [0, 100].
-100 <= Node.val <= 100
Follow up: Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?
给你一棵二叉树的根节点 root ,返回其节点值的 后序遍历 。
思路
依然是迭代和递归两种做法,两种做法的时间复杂度均是O(n),空间复杂度均是O(h)。
递归没什么好讲的,直接上代码。还是用这个更完整的例子参考。
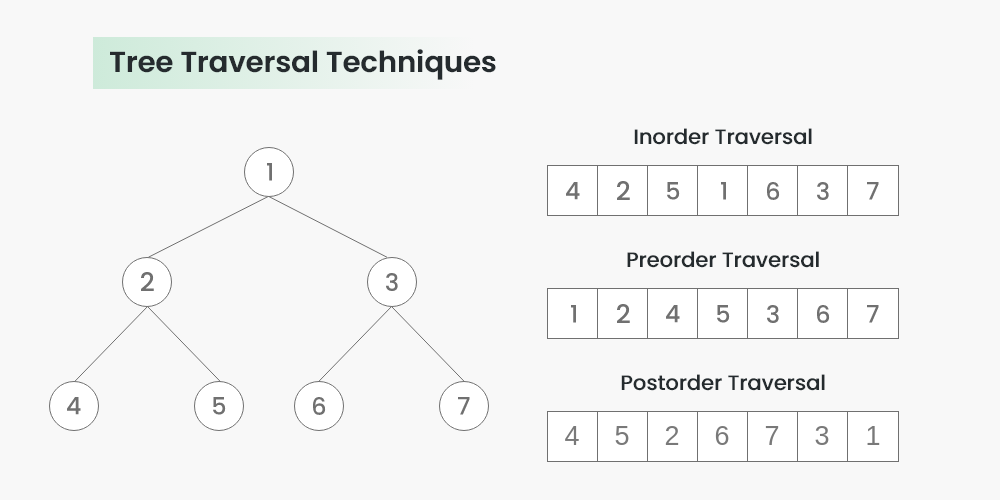
复杂度
时间O(n)
空间O(h)
代码
迭代
Java实现
1 | |
递归
Java实现
1 | |
[LeetCode] 145. Binary Tree Postorder Traversal
https://shurui91.github.io/posts/1579637700.html